Choosing the right boiler for your home is a significant decision that impacts your comfort, energy consumption, and heating costs. A well-suited boiler can efficiently heat your home and provide hot water while keeping operating expenses manageable. Here’s a guide to help you balance cost, efficiency, and compatibility with your home’s heating requirements when selecting a boiler.
1. Assess Your Home’s Heating Needs
Understanding your home’s specific heating requirements is the first step in choosing the right boiler.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Home Size: The larger the home, the more powerful the boiler needs to be to adequately heat all spaces.
- Number of Bathrooms: The demand for hot water increases with the number of bathrooms, which can impact the type of boiler you should choose.
- Insulation: Well-insulated homes retain heat better, which can reduce the size of the boiler needed for efficient operation.
- Existing System: Determine whether your current system is suitable for a boiler upgrade or if additional work is required to install a different type.

2. Types of Boilers
There are three main types of boilers to consider: combi (combination), system, and conventional. Each has distinct advantages and is suited to different home scenarios.
Combi Boilers:
- Best For: Smaller to medium-sized homes with one or two bathrooms.
- How It Works: Provides both heating and hot water directly from the unit without the need for separate tanks or cylinders.
- Advantages: Compact, space-saving, and provides hot water on demand.
- Disadvantages: Limited capacity for simultaneous hot water use in large homes.
System Boilers:
- Best For: Medium to large homes with higher hot water demands.
- How It Works: Requires a hot water storage cylinder but no loft tank, making it a good fit for homes without space in the loft.
- Advantages: Can supply hot water to multiple taps or showers at the same time.
- Disadvantages: Hot water may run out if the cylinder is depleted.
Conventional Boilers (Regular/Heat-Only):
- Best For: Large homes with high hot water demands and existing traditional heating systems.
- How It Works: Uses a cylinder and a tank in the loft for hot water storage.
- Advantages: Can handle high hot water usage simultaneously.
- Disadvantages: Requires more space and can take longer to heat water.
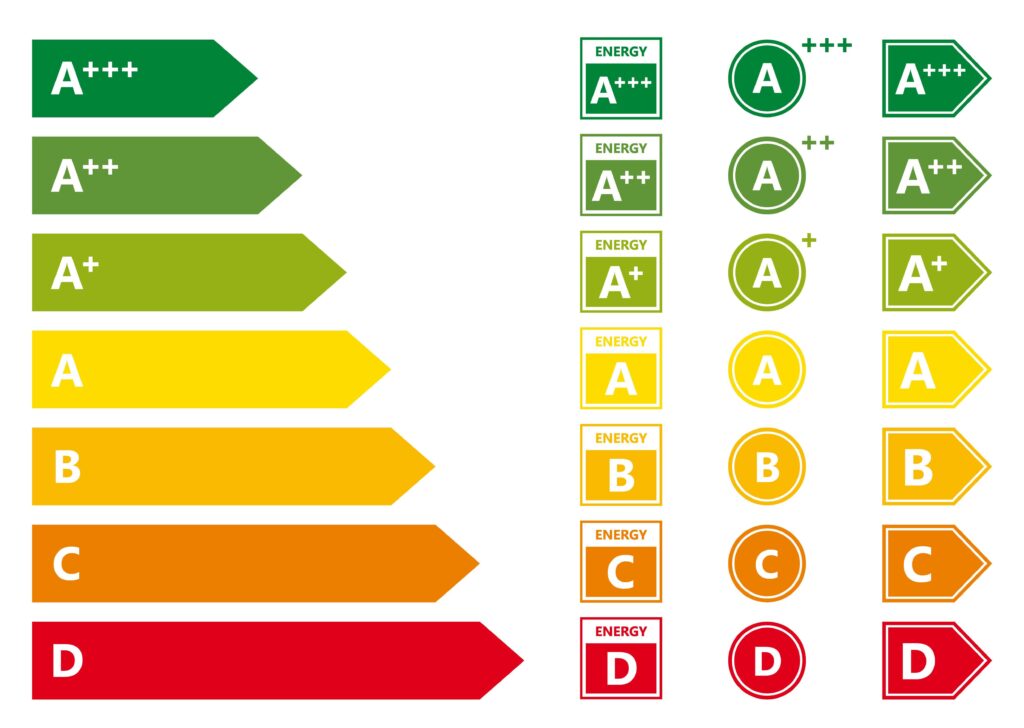
3. Energy Efficiency Ratings
The efficiency of a boiler is a key consideration, as it affects both energy consumption and utility bills. Boilers are rated for their energy efficiency using the Seasonal Efficiency of Domestic Boilers in the UK (SEDBUK) or Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) ratings.
Look for High-Efficiency Ratings:
- Condensing Boilers: These are the most energy-efficient models, using a heat exchanger to recover heat from exhaust gases.
- Efficiency Standards: Aim for a boiler with an efficiency rating of 90% or higher. High-efficiency boilers reduce fuel consumption and lower energy bills.
Energy-Saving Features:
- Modulating Burners: These adjust the amount of fuel used based on the heating demand, improving efficiency.
- Programmable Thermostats: Pairing a boiler with a smart thermostat allows for better temperature control and energy savings.
4. Fuel Type
The type of fuel your boiler uses impacts operating costs and environmental considerations.
Common Fuel Types:
- Natural Gas: Widely used and often the most cost-effective option.
- Oil: Suitable for homes without access to natural gas but generally more expensive and less eco-friendly.
- Electric: Efficient and compact but may have higher running costs depending on electricity rates.
- LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas): Offers an alternative for areas not served by the gas grid.
- Biomass: A renewable option that uses organic materials like wood pellets, but it requires more space and regular maintenance.
Choosing the Right Fuel:
- Availability: Choose a fuel type that is readily available in your region.
- Cost: Compare the long-term running costs of each fuel type.
- Sustainability: If environmental impact is a priority, consider electric or biomass boilers.
5. Budget and Installation Costs
Balancing the initial investment and long-term costs is essential.
Initial Costs:
- ombi Boilers: Typically have a lower upfront cost due to fewer components.
- System and Conventional Boilers: Higher initial costs because of the need for additional equipment like cylinders and tanks.
Installation:
- Complexity of Installation: A straightforward replacement of the same type of boiler is usually cheaper than converting to a different system.
- Associated Upgrades: Consider potential costs for additional work such as new pipework or upgrading the central heating system.
Long-Term Costs:
- Energy Efficiency: A higher-efficiency boiler may have a higher initial cost but can save money over time through reduced energy bills.
- Maintenance: Boilers that require frequent servicing or repairs can add to long-term expenses. Choose a model known for reliability and easy maintenance.

6. Space and Location
The amount of space available in your home can influence the type of boiler you choose.
Combi Boilers:
- Pros: Compact and ideal for smaller homes with limited space.
- Cons: Not suitable for homes that require a large volume of hot water at the same time.
System and Conventional Boilers:
- Pros: Suitable for homes with more space and higher hot water demands.
- Cons: Require room for additional components like a hot water cylinder or loft tank.
7. Additional Features and Considerations
To maximize efficiency and convenience, consider modern features that enhance the functionality of your boiler.
Smart Controls:
- Remote Control: Wi-Fi-enabled boilers can be controlled via apps, providing better control over heating schedules and energy use.
- Weather Compensation: Adjusts boiler output based on outdoor temperature for improved efficiency.
Warranty and Support:
- Long Warranty Periods: Look for boilers with warranties of at least 5-10 years for peace of mind.
- Reputable Brands: Choose boilers from trusted manufacturers known for reliability and customer service.
Conclusion
Selecting the right boiler involves evaluating your home’s heating needs, energy efficiency goals, budget, and available space. Combi boilers are best for smaller homes with moderate hot water usage, while system boilers cater to medium to large homes. Conventional boilers are ideal for larger homes with high hot water demand. Consider factors like fuel type, installation complexity, and long-term maintenance to make an informed choice. Consulting with a professional HVAC technician can help you identify the best option for your home and ensure a seamless installation.