Choosing the right boiler for your home is essential for maintaining comfort, energy efficiency, and long-term cost savings. With a wide range of options on the market, it can be difficult to know where to start. Here’s a guide to the key factors homeowners should consider when selecting a new boiler.
1. Boiler Size
Boiler size refers to the output capacity, measured in kilowatts (kW), which directly impacts how well it can heat your home and supply hot water.
Key Considerations:
- Home Size: Larger homes with more rooms and bathrooms will require a boiler with a higher kW output to meet heating and hot water needs effectively.
- Heating Needs: Consider the number of radiators and the frequency of hot water use. Oversized boilers can lead to energy wastage, while undersized ones may struggle to meet demand.
How to Choose:
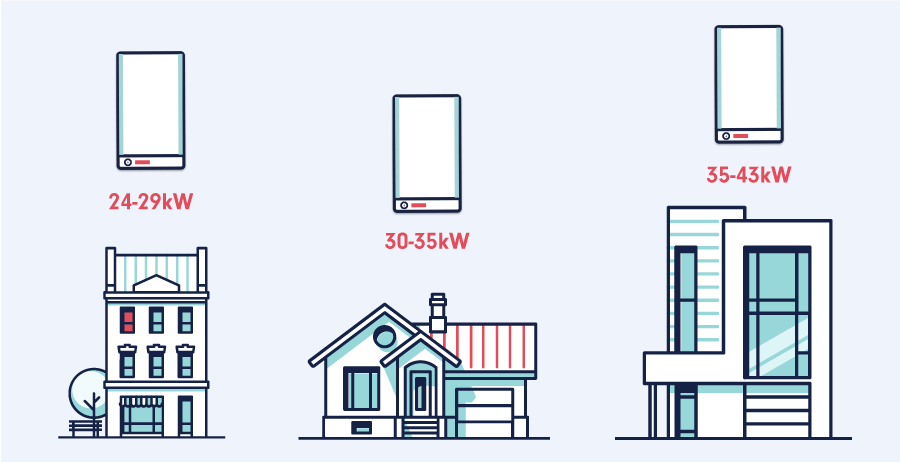
- Small Homes/Apartments: Typically need a boiler between 24-30 kW.
- Medium-Sized Homes: May require a 30-35 kW boiler.
- Large Homes: Often benefit from boilers in the 35-42 kW range.
- Consult a Professional: Have an HVAC technician assess your home’s specific heating needs to determine the right size.
2. Efficiency Rating
Boiler efficiency is crucial for reducing energy bills and environmental impact. Modern boilers come with ratings that indicate how well they convert fuel into heat.
Types of Efficiency Ratings:
- Seasonal Efficiency of Domestic Boilers in the UK (SEDBUK): Rates boilers on an A-G scale, with A being the most efficient.
- Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE): Common in the US, this rating shows the percentage of energy used for heating. Look for boilers with an AFUE rating of at least 90% for optimal efficiency.
Why It Matters:
- Lower Energy Costs: High-efficiency boilers use less fuel to produce the same amount of heat, translating to savings on utility bills.
- Environmental Benefits: Efficient boilers produce fewer emissions, reducing your household’s carbon footprint.
3. Fuel Type
The type of fuel your boiler uses can affect its efficiency, operating costs, and environmental impact.
Common Fuel Types:
- Natural Gas: The most popular fuel type, offering a reliable and cost-effective heating solution.
- Oil: Suitable for homes without access to a natural gas line, though generally more expensive and less eco-friendly.
- Electricity: Electric boilers are highly efficient and environmentally friendly when powered by renewable energy, but they can be costly to operate depending on electricity rates.
- LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas): Offers a good alternative for remote areas not served by the gas grid.
- Biomass: A renewable option using organic materials like wood pellets. It is eco-friendly but requires more maintenance and space for fuel storage.
Choosing the Right Fuel:
- Availability: Choose a fuel type that is easily accessible in your area.
- Budget: Consider both upfront and long-term fuel costs.
- Eco-Concerns: Opt for biomass or electric if sustainability is a priority for you.

4. Type of Boiler
There are different types of boilers, each with unique features that may make them more or less suitable for your home.
Types of Boilers:
- Combi Boilers: Combine water heating and central heating in one unit, providing hot water on demand without the need for a separate tank. Ideal for smaller homes.
- System Boilers: Require a separate hot water storage cylinder but do not need a water tank in the loft. Suitable for medium to large homes with multiple bathrooms.
- Conventional Boilers: Also known as regular or heat-only boilers, they use both a tank and a cylinder. Best suited for homes that need large amounts of hot water at the same time.
- Condensing Boilers: Can be any of the above types but are designed to be more energy-efficient by capturing and reusing heat that would otherwise be lost.
Considerations:
- Space: Choose a combi boiler if space is limited. For larger homes, a system or conventional boiler may be more practical.
- Hot Water Needs: If your household uses hot water simultaneously in multiple locations, a system or conventional boiler is better than a combi boiler.
5. Budget and Installation Costs
The upfront cost of the boiler and the installation expenses are significant factors in your decision-making process.
Budget Breakdown:
- Initial Cost: This includes the price of the boiler and any additional components needed, such as tanks or cylinders.
- Installation: Professional installation can vary widely in cost, depending on the complexity and the installer’s rates.
- Operating Costs: Consider the ongoing cost of fuel, maintenance, and potential repairs.
Tips for Budgeting:
- Get Multiple Quotes: Compare prices from different installers to ensure you’re getting a fair deal.
- Look for Rebates and Incentives: Many regions offer rebates for purchasing energy-efficient boilers, which can offset the initial investment.

6. Smart Features
Modern boilers often come with smart technology that allows for better control and energy savings.
Features to Look For:
- Programmable Thermostats: Schedule your heating to match your routine, saving energy when you’re not home.
- Smart Integration: Wi-Fi-enabled boilers can be controlled via smartphone apps, offering more convenience and optimizing energy use.
- Modulating Technology: Boilers with modulating burners can adjust output based on current demand, enhancing efficiency and comfort.
Conclusion
Choosing the right boiler for your home involves balancing size, efficiency, fuel type, budget, and your household’s specific needs. Taking the time to research and understand these factors will help you make an informed decision that ensures comfort, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for years to come. Always consult with a professional HVAC technician to confirm that your chosen boiler is the best fit for your home and heating requirements.
