Selecting the right boiler is essential for keeping your home warm, ensuring a reliable hot water supply, and maintaining energy efficiency. With various options available, understanding the differences between combi, system, and conventional boilers can help you make an informed choice that suits your heating requirements. Here’s a comprehensive guide comparing these boiler types and recommendations on how to choose based on home size, number of bathrooms, and heating needs.
1. Combi Boilers
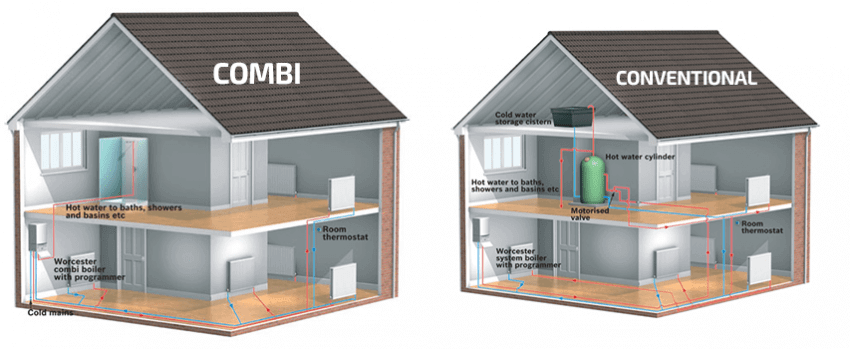
Overview: A combi (combination) boiler is a compact unit that provides both central heating and hot water on demand without the need for separate water storage tanks or cylinders.
Advantages:
- Space-Saving: Ideal for smaller homes or apartments as it does not require a hot water cylinder or loft tank.
- Hot Water On-Demand: Provides instant hot water as it heats water directly from the mains supply.
- Energy Efficiency: Combines heating and water heating, reducing energy consumption and lowering utility bills.
Disadvantages:
- Simultaneous Use Limitations: May struggle to supply adequate hot water if multiple taps or showers are used at once.
- Not Ideal for Large Homes: Limited capacity may not meet the hot water demands of larger households.
Best For:
- Small to Medium Homes: Properties with one or two bathrooms and moderate heating needs.
- Space-Conscious Households: Homes with limited space for additional tanks or cylinders.
2. System Boilers
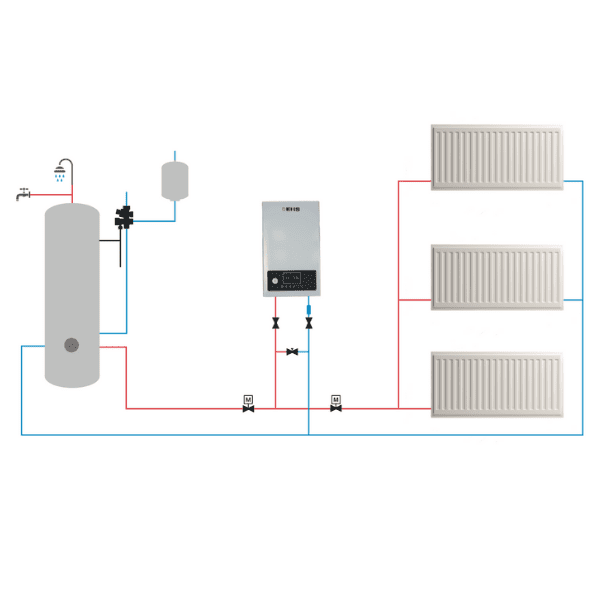
Overview: System boilers, also known as sealed system boilers, heat water directly from the mains and store hot water in a separate cylinder. This setup allows for a consistent supply of hot water to multiple outlets simultaneously.
Advantages:
- Hot Water for Multiple Bathrooms: Can easily handle the hot water demand of homes with multiple bathrooms.
- Compact Design: Requires less space than conventional systems since it doesn’t need a loft tank, but it does require a hot water cylinder.
- Good Energy Efficiency: Modern system boilers are designed to be efficient and maintain a steady supply of hot water.
Disadvantages:
- Requires Space for a Cylinder: Although it saves space compared to conventional boilers, it still needs a dedicated area for the hot water cylinder.
- Limited Hot Water Supply: Hot water can run out if the cylinder is depleted, requiring a wait for it to refill and reheat.
Best For:
- Medium to Large Homes: Ideal for properties with two or more bathrooms that need simultaneous access to hot water.
- Families with High Hot Water Usage: Households where multiple showers or taps are in use at the same time.
3. Conventional Boilers
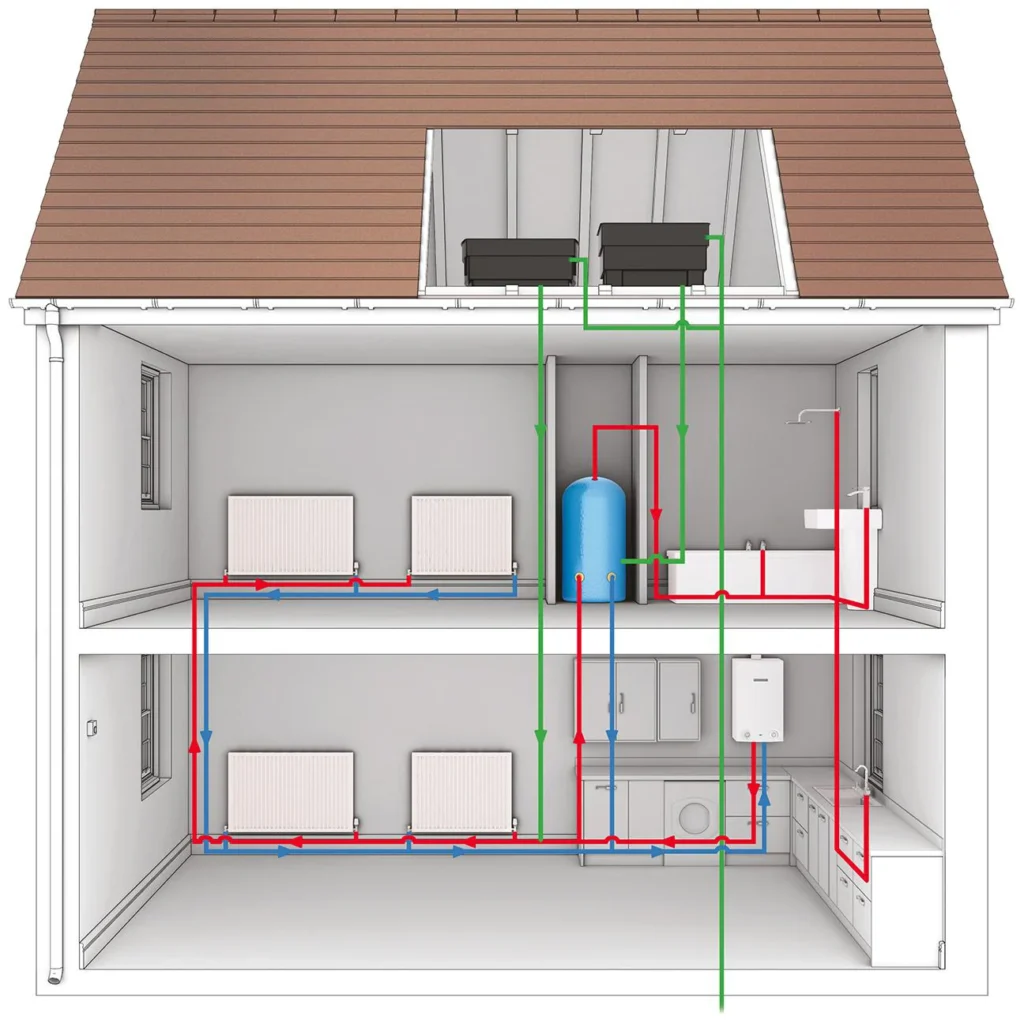
Overview: Conventional boilers, also known as regular or heat-only boilers, use both a hot water cylinder and a cold water storage tank in the loft. This setup allows for a high volume of hot water to be stored and used as needed.
Advantages:
- Suitable for High Hot Water Demand: Can supply hot water to multiple bathrooms simultaneously without a significant drop in pressure.
- Ideal for Older Homes: Works well with traditional heating systems that include a separate water tank and cylinder.
- Reliable for Large Properties: Provides ample hot water for larger households.
Disadvantages:
- Requires More Space: Needs both a loft tank and a cylinder, which can be impractical for homes with limited space.
- Lower Energy Efficiency: Not as energy-efficient as combi or system boilers, as hot water stored in the cylinder can lose heat over time.
- Longer Heating Times: Takes time to heat and store hot water, unlike the on-demand capabilities of a combi boiler.
Best For:
- Large Homes with High Water Demand: Properties with three or more bathrooms and a need for substantial hot water storage.
- Homes with Existing Conventional Systems: Upgrading a similar system can be more straightforward and cost-effective.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Boiler
- Home Size:
- Small Apartments or Homes: A combi boiler is likely the best fit due to its compact design and ability to provide on-demand hot water.
- Medium Homes: System boilers can handle higher demand and are suitable for homes with multiple bathrooms.
- Large Homes: Conventional boilers are often the most practical solution for large properties that require hot water across many bathrooms.
- Number of Bathrooms:
- One Bathroom: A combi boiler is usually sufficient.
- Two Bathrooms: A system boiler offers better performance for homes with two bathrooms used simultaneously.
- Three or More Bathrooms: A conventional boiler or a high-capacity system boiler is recommended to meet high hot water demand.
- Hot Water Usage:
- Low to Moderate Usage: A combi boiler can cover typical needs efficiently.
- High Usage with Simultaneous Demands: A system or conventional boiler is better equipped to handle large-scale hot water needs.
- Space Constraints:
- Limited Space: Combi boilers save the most space by not requiring a separate cylinder or tank.
- Ample Space: Conventional boilers can be installed if your home has a loft and enough room for a cylinder.
- Budget:
- Initial Cost: Combi boilers generally have a lower initial cost compared to system and conventional boilers due to fewer components.
- Running Costs: Combi boilers are more energy-efficient for smaller households, while system boilers can be more economical for homes with consistent high water use.
Conclusion
Choosing the right boiler for your home requires assessing your heating and hot water needs, the size of your property, and the space available for installation. Combi boilers are ideal for smaller homes with one bathroom, system boilers are a good fit for medium-sized homes with multiple bathrooms, and conventional boilers are best for large homes with high water demand. Consulting with a professional HVAC technician can help you make the best choice for your specific situation and ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
